VITAMIN D - TYPES, DOSAGE, HEALTH BENEFITS, SIDE EFFECTS [SCIENCE EXPLAINED]
Vitamins are substances that your body needs to grow and develop normally. There are 13 vitamins your body needs.
Every vitamin has its own function which an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism. Essential nutrients cannot be synthesized in the organism so they must be consumed through diet.
So today we will only talk about Vitamin D in this article and try to figure out what is the importance of Vitamin D and we can use it.
WHAT IS VITAMIN D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble essential vitamin that our skin synthesizes when exposed to the sun. It is one of the 24 micro-nutrients that are crucial for human survival.
It benefits us in many ways, from bone health to mood.
The sun is the major natural source of the nutrient, but vitamin D is also found naturally in fish and eggs. It is also added to dairy products.

Most people are not deficient in vitamin D, but they do not have an optimal level of vitamin D either.
Due to the many health benefits of vitamin D, supplementation is encouraged if optimal levels are not present in the body.
Vitamin D is a essential fat soluble vitamin, has a lot of health benefits ranging from bone health to mood. The main source of vitamin D is sun exposure but can be found in foods as well as supplements also.
TYPES OF VITAMIN D?
There are mainly two forms in which Vitamin D is available i.e. Vitamin D2 and Vitamin D3.

VITAMIN D2
Vitamin D2 is known as ergocalciferol. Vitamin D2 mainly comes from plant sources and fortified foods.
Vitamin D2 is cheaper to produce, it’s the most common form in fortified foods.
Sources of Vitamin D2
- Mushrooms (grown in UV light)
- Fortified foods
- Dietary supplements
Vitamin D3
Vitamin D3 is also known as cholecalciferol. Vitamin D3 is only found in animal-sourced foods. Most of the health benefits are seen from Vitamin D3 supplementation.

Sources of Vitamin D3
- Oily fish and fish oil
- Liver
- Egg yolk
- Butter
- Dietary supplements
Vitamin D comes in two forms Vitamin D2(ergocalciferol) and D3(cholecalciferol). Vitamin D2 comes from plant sources while vitamin D3 found in animal sources. However, while most of the health benefits provided by Vitamin D3.
HOW MUCH VITAMIN D SHOULD I TAKE?
According to National Academies of Sciences, is the recommended daily allowance (RDA) of 600 IU (international unit) per day for both children and adults up to age 70.
The Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for Vitamin D is currently set at 600–800 IU/day (15–20 mcg) for adults.

Even consuming 1000 IU of vitamin D has seen a lot of health benefits like increased bone mineral density, good mood , improved sleep etc.
According to RDA, 600- 800 IU of vitamin is recommended to general population. Even consuming 1000 IU of vitamin D a day has a lot of health benefits like bone strength, good sleep, etc.
VITAMIN D FROM SUNSHINE ?

The body produces vitamin D from cholesterol, provided there is an adequate amount of UV light from sun exposure.
In order to maintain a healthy vitamin D level. Sun exposure can be bolstered with vitamin D rich foods and supplements to attain sufficient levels.
Your body can produce vitamin D when the skin is exposed to ultraviolet B rays.
Generally speaking, 5 to 30 minutes of unprotected sun exposure to the hands, face, and arms at least three times a week between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m. is considered enough to keep blood vitamin D levels out of the deficient range.

Keep in mind that longer periods of unprotected sun exposure don’t necessarily lead to higher vitamin D production, as the Ultra violent rays will eventually cause the vitamin D in your skin to degrade to an inactive state.
In addition to an appropriate dose of sun exposure, you can increase vitamin D through diet and supplementation. Diet and supplementation strategies will be particularly important for those who live in areas of low sun exposure .
An average person will need 5–30 minutes of unprotected sun exposure to the hands, face, and arms at least three times a week between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m to keep your vitamin D levels out of the deficient range. To increase your vitamin D levels, combine amount of sun exposure to dietary sources of vitamin D and supplementation.
VITAMIN D IS GOOD FOR YOU?

Supplementing vitamin D is associated with a wide range of benefits, including increased cognitive output, immune health, bone health and well-being.
Supplementation can also reduce the risks of cancer, heart disease and diabetes.
People deficient in vitamin D may also experience increased testosterone levels after supplementation.
The original RDA of vitamin D, ~400 IU/day, was actually the minimum you need to not get rickets. The above benefits usually come from higher levels of vitamin D in the body, which can be usually obtained with roughly 2000 IU/day.
Overall, vitamin D is both cheap and safe (is not toxic except at very high levels). While it may not fix everything, it has enough benefits to warrant taking.
Vitamin D supplementation has a host of positive benefits. One must consider both the full body of research and also look past the quantitative and consider the qualitative. Vitamin D is cheap, safe, effective, and most people are in a deficient state. If you do not get enough direct sunlight exposure, supplementation is a great choice.
BENEFITS OF VITAMIN D SUPPLEMENTATION
1. VITAMIN D MAY REDUCES THE RISK OF FALLS and fracture IN ELDERLY PEOPLE
Risk of falling refers to elderly individuals with functional impairment, and interventions to improve muscular function tend to reduce falls and thus reduce both fracture and mortality risk.

Fracture risks were reduced when studies were controlled for studies above 400 IU only.
Vitamin D supplementation decreases falls and fractures. The bottom line is that we care most about preventing fractures and subsequent death. The people most at-risk for those are the elderly, and several studies show that vitamin D helps prevent such falls.
A decrease in bone fracture risk appears to exist when supplemental doses of Vitamin D3 are taken above 800 IU, with this protective effect being highly correlated with the improvement in functionality and fall reduction risk.
Most of the research has been done in the 700-1000 IU range.
The risk of falls in the elderly (and rate of bone fractures) appears to be significantly reduced with Vitamin D supplementation at 700 IU or greater.
Supplementing Vitamin D 700-800 IU or more may reduces the risk of fall and reduce the risk of bone fracture in elderly adults. A overall improvement in functionality and mobility also seen.
2. Vitamin D may prevent acute respiratory infections and asthma

Asthma is a condition in which your airways narrow and swell and may produce extra mucus. This can make breathing difficult and trigger coughing and shortness of breath
Studies suggest that there is potential benefit of vitamin D to prevent acute respiratory infections.
Study had limited power to detect the effects of vitamin D supplementation on the risk of upper respiratory infection.
Vitamin D supplementation was safe, and it protected against overall respiratory system.
A protective effect against asthma was found, but not for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Overall, the studies were of low risk for bias.
Positive effect of vitamin D supplementation on the risk of acute respiratory infections. Persons with higher serum vitamin D appear to have less frequency asthmatic attacks relative to persons with lower Vitamin D levels.
3. Vitamin D may help you in cure depression
Many people get depressed during the winter months, when we produce less vitamin D. So, can supplemental vitamin D will not cure depression but it may help.

Supplemental vitamin D is relatively cheap and safe, and may provide a variety of health benefits beside brightening your mood.
But depression is complex. There are many possible causes.
Insufficient vitamin D levels in body is associated with depression.
If your levels of vitamin D are sufficient, however, then whether your depression is severe or not, supplementation isn’t likely to help.
The observational data suggests a correlation between depression and low levels of vitamin D, but that doesn’t mean that low levels of vitamin D cause the depression.
It might be that depressed people go outside less, thus getting less sunlight, thus producing less vitamin D.
The depression would then be the cause of the low vitamin D levels, rather than its consequence.
Low levels of vitamin D (found in more than 40% of Americans) have been associated with depression.
Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with depression. The decrease in vitamin D production caused by reduced sunlight during the winter months. If your vitamin D levels are not low, supplementation isn’t likely to benefit your mood. If they are low, supplementation is more likely to help.
4. Vitamin D may increase testosterone levels

Testosterone is the best-known androgen (male hormone), but females produce it too. In both sexes, low testosterone can reduce libido and cause fat gain, muscle loss, and bone loss.
Studies seen that men who were taking 3,332 IU of vitamin D for one year, were resulted in increased testosterone. Bio-active and free testosterone also increased.
An increase in testosterone has been noted in men with 3,332 IU of Vitamin D over the course of a year.
5. Vitamin D may increase power output and take less time to recover
Power output is defined as the strength you can generate in the shortest amount of time. It is associated with activating or using the type-II muscle fibers.

20 healthy males were supplemented with 4000 IU vitamin D.
All experienced muscle damage through eccentric quad(leg) exercises. Post-damage was measured at two different speeds up to 7 days after the eccentric exercise.
Soreness(pain) was recovered more quickly in the supplemented group at slower speeds, and trended toward significance at quicker speeds.
Although a trend to increase power output has been noted, most research suggest no benefit, although recovery times may improve.
Healthy men who are involved in some kind of resistance/weight training, supplementing vitamin D is associated with increase in power output and take less time to recover.
6. SUPPLEMENTING VITAMIN D MAY IMPROVE SLEEP QUALITY
The optimal amount of sleep varies from person to person.
Most adults require least seven hours per night on a regular basis.

Sleeping less than this is associated with numerous adverse health outcomes, including cardiovascular diseases, impaired immune function, impaired cognitive performance, and even death.
Observational evidence has suggested a correlation between sleep quality and vitamin D levels, some studies suggest that vitamin D supplementation improve sleep quality.
The sleep quality improved in participants taking the vitamin D supplement. Blood levels of vitamin D increased in those taking the supplements.
The vitamin D group had a significantly greater improvement in sleep quality.
Vitamin D supplementation may improve sleep quality in people who have moderately low levels of vitamin D. Vitamin D may also help us to overcome the problems which we face due to lack of sleep.
7. Vitamin D and cardiovascular disease prevention
Vitamin D levels in our body was an independent predictor of all cause mortality and cardiovascular disease.

There appears to be less risk of cardiovascular disease and related cardiovascular complications with supplementation of 1,000 IU of Vitamin D or higher levels of Vitamin D.
Both the high prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in the general population and the identification of the vitamin D receptor in the heart and blood vessels raised interest in the potential cardiovascular effects of vitamin D.
Experimental studies have demonstrated various cardiovascular protective actions of vitamin D, but vitamin D intoxication in animals is known to induce vascular calcification.
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased cardiovascular risk.
Currently available evidence support cardiovascular benefits from vitamin D supplementation with the commonly used doses. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased cardiovascular risk.
8. Vitamin D Is Associated with Greater Muscle Strength in Healthy Men and Women
Vitamin D was significantly associated with arm and leg muscle strength when controlling for age and gender.

Vitamin D remained directly related to both arm and leg strength.
Data suggest that there may be a differential effect of vitamin D on upper and lower body strength.
Studies supports a direct relation between vitamin D and muscle strength.
Supplementing vitamin D may help you in increased strength. Studies supports a direct relation between vitamin D and muscle strength. This resulted may be due to increased in bone mineral density.
side effects from too much vitamin d (TOXICITY)

This increase in vitamin D supplementation is due to a growing awareness of widespread vitamin D deficiency and scientific data suggesting the beneficial effects of vitamin D in various diseases.
Due to increased global recognition of vitamin D deficiency in the general population, individuals are more concerned about vitamins D levels in their body.
However, the increasing use of vitamin D treatments has also seen a substantial increase in the number of reports of vitamin D intoxication.
Vitamin D toxicity is a rare occurrence caused by over supplementation. Patients and prescribers should be more aware of the potential dangers of vitamin D overdose.
The underlying causes included manufacturing errors, overdosing by patients or prescribers, and combinations of these factors.

Even up to the intake of vitamin D supplementation 20,000 IU/day, did not demonstrate any signs of toxicity.
Most of the reported patients showed symptoms of vitamin D toxicity such as vomiting, dehydration, pain, and loss of appetite.
In children and adolescents, vitamin D toxicity is rare and usually asymptomatic.
Vitamin D toxicity is rare, mainly caused by manufacturer error or prescriber's mistake. Even upto the intake of vitamin D supplementation 20,000 IU/day, did not demonstrate any signs of toxicity. Vitamin D toxicity symptoms may include such as vomiting, dehydration, pain, and loss of appetite.
SOME NATURAL GOD SOURCES D VITAMIN D
Vitamin D is vital for bone health and its deficiency deemed as a disease of the past has re-emerged as an important health concern.
Exposure of the skin to solar ultraviolet B radiation(sunshine) is the major source of vitamin D and only a small proportion is derived from dietary intake.
Vitamin D, also known as the sunshine vitamin.
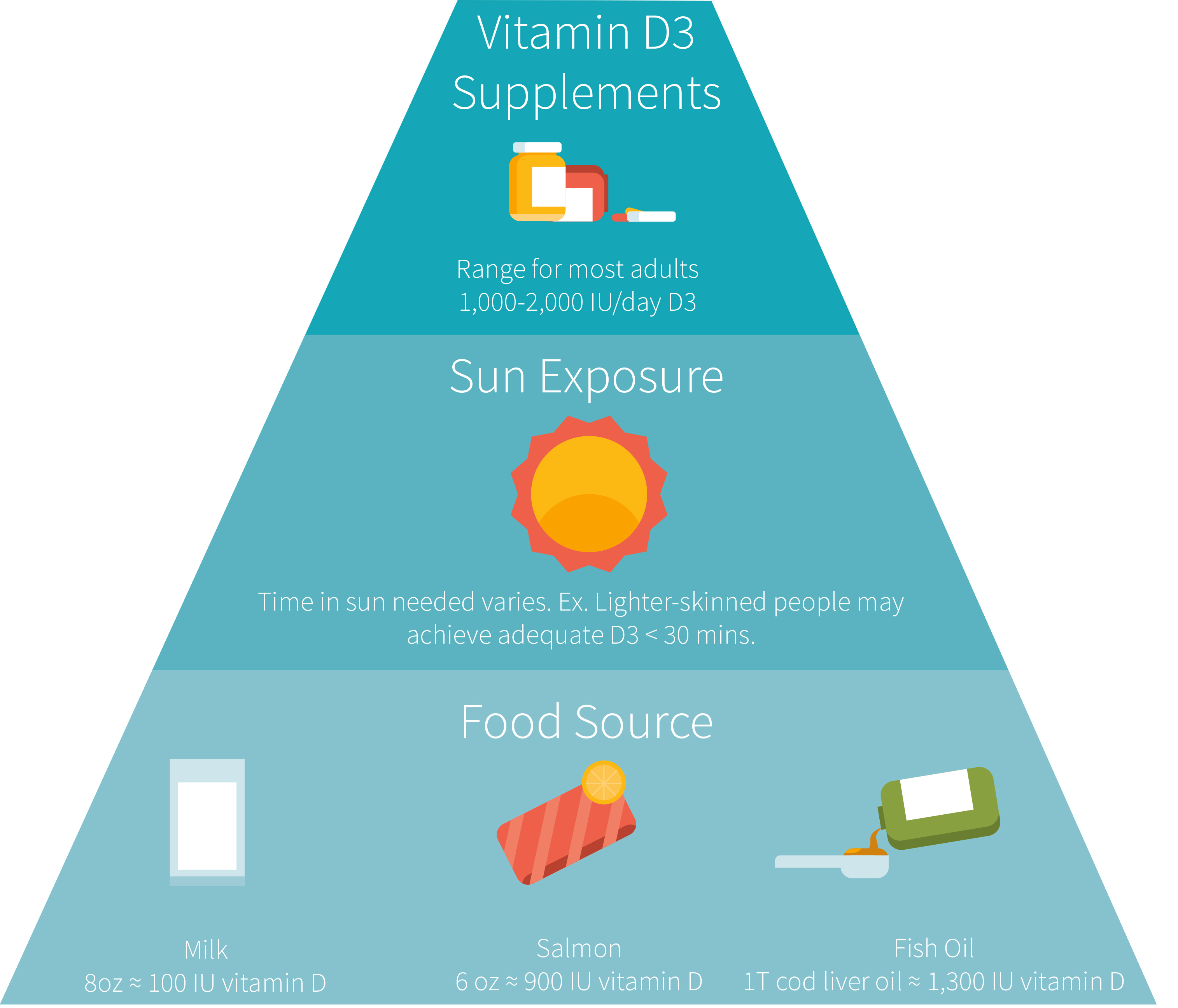
Animal foodstuffs (e.g., fish, meat, offal, egg, dairy) are the main sources for naturally occurring cholecalciferol (vitamin D3).
Egg yolks can provide significant amounts of vitamin D gives you around 18–39 IU of vitamin D.
Cheese is a natural source of vitamin D, albeit in very small amounts. 8–24 IU
Cow’s milk. Depending on the country you live in, you can expect 1 cup (240 ml) of milk to contain up to 120 IU (3 mcg) of vitamin D
Yogurt. Some dairy and nondairy yogurts are fortified in vitamin D, giving around 52 IU (1.3 mcg).
SUMMARY
Vitamin D is a essential fat soluble vitamin, has a lot of health benefits ranging from bone health to mood. The main source of vitamin D is sun exposure but can be found in foods as well as supplements also.
Vitamin D comes in two forms Vitamin D2(ergocalciferol) and D3(cholecalciferol). Vitamin D2 comes from plant sources while vitamin D3 found in animal sources. However, while most of the health benefits provided by Vitamin D3.
According to RDA, 600- 800 IU of vitamin is recommended to general population. Even consuming 1000 IU of vitamin D a day has a lot of health benefits like bone strength, good sleep, etc.
An average person will need 5–30 minutes of unprotected sun exposure to the hands, face, and arms at least three times a week between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m to keep your vitamin D levels out of the deficient range. To increase your vitamin D levels, combine amount of sun exposure to dietary sources of vitamin D and supplementation.
Vitamin D supplementation has a host of positive benefits. One must consider both the full body of research and also look past the quantitative and consider the qualitative. Vitamin D is cheap, safe, effective, and most people are in a deficient state. If you do not get enough direct sunlight exposure, supplementation is a great choice.
Supplementing Vitamin D 700-800 IU or more may reduces the risk of fall and reduce the risk of bone fracture in elderly adults. A overall improvement in functionality and mobility also seen.
Positive effect of vitamin D supplementation on the risk of acute respiratory infections. Persons with higher serum vitamin D appear to have less frequency asthmatic attacks relative to persons with lower Vitamin D levels
The decrease in vitamin D production caused by reduced sunlight during the winter months. If your vitamin D levels are not low, supplementation isn’t likely to benefit your mood. If they are low, supplementation is more likely to help.
Healthy men who are involved in some kind of resistance/weight training, supplementing vitamin D is associated with increase in power output and take less time to recover.
Vitamin D supplementation may improve sleep quality in people who have moderately low levels of vitamin D. Vitamin D may also help us to overcome the problems which we face due to lack of sleep.
Currently available evidence support cardiovascular benefits from vitamin D supplementation with the commonly used doses. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased cardiovascular risk.
Supplementing vitamin D may help you in increased strength. Studies supports a direct relation between vitamin D and muscle strength. This resulted may be due to increased in bone mineral density.
Vitamin D toxicity is rare, mainly caused by manufacturer error or prescriber's mistake. Even up to the intake of vitamin D supplementation 20,000 IU/day, did not demonstrate any signs of toxicity.
REFERENCES
https://examine.com/supplements/vitamin-d/
https://examine.com/members/deep-dives/article/should-1000-iu-be-the-new-rda-for-vitamin-d/
https://examine.com/nutrition/sunscreen-vitamin-d/
https://examine.com/nutrition/do-i-need-to-supplement-vitamin-d-if-i-drink-fortified-milk/
https://examine.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-and-bone-mineral-density/
https://examine.com/nutrition/the-truth-about-vitamin-d/
https://examine.com/members/deep-dives/article/can-vitamin-d-crease-pain/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24414552/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27150190/
https://examine.com/members/deep-dives/article/can-supplemental-vitamin-d-improve-sleep/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30675873/
https://examine.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-and-depression/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31405892/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30042334/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29498758/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10232622/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24456284/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29668516/

Comments
Post a Comment