WHAT IS WHEY PROTEIN- BENEFITS, SIDE EFFECTS, BEST TIME TO TAKE [RESEARCHED ANALYSIS]
WHAT IS WHEY PROTEIN?

Whey protein is a type of protein which is usually present in milk. Whey protein is known for its fast digesting and absorbing properties. Apart from that whey protein is a complete source of protein which means it has all the Essential Amino Acids which is needed for our growth and overall development of our body.
Whey and casein protein are both derived from milk. Whey protein powder is extremely popular due to its high digestibility and well-researched muscle-supporting benefits.

Whey protein supplement/powder is usually taken by athletes and bodybuilders as a pre- or post-workout to enhance the Muscle Protein Synthesis rates. In short, it will help them to recover and build muscle faster.
Whey protein is the water-soluble part of milk. As a supplement, it’s sold as dry powders with various levels of processing that affect how concentrated a source of protein they are and how fast they’re absorbed.
Whey is a high-quality source of protein rich in the amino acid cysteine, which can bolster the body's antioxidant defenses, and glutamine, which can benefit intestinal health.
WHAT IS WHEY PROTEIN POWDER MADE OUT OF ?
Whey and casein protein are both derived from milk. Whey protein powder is extremely popular due to its high digestibility and well-researched muscle-supporting benefits.

Cow milk protein is 80% casein and 20% whey protein. In your stomach, casein forms a gel and thus digests slowly. The protein in cheese is mostly casein. a byproduct of cheesemaking.
When a coagulant (usually renin) is added to milk, casein and whey separate.
Whey Protein is the water-soluble part of milk. As a supplement, it’s sold as dry powders with various levels of processing that affect how concentrated a source of protein they are and how fast they’re absorbed.
HOW MUCH PROTEIN YOUR BODY NEEDS IN A DAY ?
The amount of protein your body needs in day is depends in many factors like age, gender, body fat percentage, your goal (bulk or cut), level of physical activity, etc.
According to ICMR guidelines if a person is having a normal sedentary life-style he/she will need around 0.8-1 gram/kg of body weight. For example, for a 60 kg person it comes out to be around 48-60 gram of protein a day.
According to some studies, If an individual is involved in some kind of resistance training he/she will need around 1.6-2.2 gram/kg. For example, for a 60 kg person it comes out to be 96-132 gram of protein in a day.
BENEFITS OF WHEY PROTEIN
HITTING DAILY PROTEIN INTAKE
The main benefit of whey protein supplement is that it can help you to hitting your daily protein intake without getting the extra calories from food.

If you're into any kind of weight training or resistance training you will be needing 1.6-2.2 gram of protein per kg in a single day.
For a 80 kg person, who is having a healthy body fat percent range (14-18%) will be needing 130-180 grams of protein a day.
On an average, 1 scoop of whey protein contain around 25 grams of protein. So if you're able to extract 100 grams of protein from food itself. So supplementing 1-2 scoops of whey protein powder can help you in hitting your daily protein intake.
Note: Whey protein should only be used as a supplement, there is no replacement of food. Food contains several vitamins minerals and several other nutrients also which is needed for your overall mind and body development. It is recommended that supplement should be only account for 10-15% of the daily caloric intake.
PREVENTS MUSCLE LOSS

When you are in a caloric deficit state, while loosing fat there are high chances that you will also loose muscle at the same time.
Your body is in a energy deficit state so to give your body sufficient energy, protein molecules will convert into amino acids so they can provide energy. This happens in most of the cases while in a deficit, so in order to avoid that you need to consume sufficient amount of protein on daily basis.
Current research suggests that dietary protein supplementation can augment resistance exercise-mediated gains in lean muscle mass and strength and can preserve muscle mass during periods of diet-induced energy restriction (caloric deficit).
Perhaps less appreciated, whey protein supplementation can augment resistance training-mediated gains in lean muscle mass even in individuals habitually consuming 'adequate' (i.e., >0.8 g/ kg /day) protein.
Additionally, overfeeding energy with moderate to high-protein intake (15-25 % protein or 1.8-3.0 g /kg/day) is associated with lean mass, but not increase in fat mass, when compared to overfeeding energy with low protein intake (5 % protein or ~0.68 g/ kg/ day).

after knowing this. you are like
GAINING FAT FREE MASS IN OLDERLY ADULTS

In older individuals there is reductions in muscle mass and physical function. Also the Muscle protein synthesis response to amino acid administration and physical activity is low.
Although resistance training is an effective way to slow down muscle breakdown(muscle loss) in the elderly
There are studies that shows a combination with protein supplementation could offer additional benefits to an older population.

According to a study, where 459 men were taken between the age group of 69-79 years and they were performing resistance training with protein supplementation for 8 weeks.
It was found that, Protein Supplementation in combination with resistance training was associated with gains in fat-free mass.
Combining protein supplementation with resistance training is effective for eliciting gains in fat-free mass among older adults, but does seem to increase muscle mass or strength but in a very small amount.
INCREASED MUSCLE MASS

Whey Protein supplements are frequently consumed by athletes and recreationally active adults to achieve greater gains in muscle mass and strength and improve physical performance.
According to some researches, For untrained individuals, consuming supplemental protein likely has no impact on lean mass and muscle strength during the initial weeks of resistance training.

However, as the duration, frequency, and volume of resistance training increase, Whey Protein Supplementation may promote muscle hypertrophy and enhance gains in muscle strength in both untrained and trained individuals.
Evidence also suggests that protein supplementation may accelerate gains in both aerobic and anaerobic power in healthy adults.
RECOVERY FROM MUSCLE DAMAGE AND SORENESS
Amino acids are like building blocks of our muscle cell, in order to maintaining or grow that muscle you need to consume protein so it can help you in building more blocks.
If someone is doing any type of resistance training, then they need more protein and rest in order to recover from that muscle damage.
Overwhelmingly, studies have consistently demonstrated the acute benefits of Whey Protein Supplementation on post-exercise muscle anabolism.
Which may facilitate the recovery of muscle function and performance.
However, to date, when protein supplements are provided, acute changes in post-exercise protein synthesis and anabolic responce can be seen.
Researches also have been shown have resulted in measurable reductions in muscle damage and enhanced recovery of muscle function.
INCREASES MUSCLE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS RATE
WHAT IS MUSCLE PROTEIN SYNTHESIS?
Protein is the main building block of your muscle.
When you ingest protein, the protein is digested into amino acids. These amino acids are absorbed in the gut and subsequently released into the circulation.

Protein synthesis is the process of building new proteins. This process happens in all organs.
Muscle protein synthesis is the process of building specifically muscle protein. Think of a muscle as a wall. Each brick is an amino acid. Muscle protein synthesis is the addition of new bricks to the wall.
Protein sources differ in their capacity to stimulate MPS. The main properties that determine the anabolic effect of protein are it’s rate of digestion and it’s amino acid composition (particularly leucine).
This is best illustrated by study which compared the muscle protein synthetic response to casein, casein hydrolysate and whey protein.
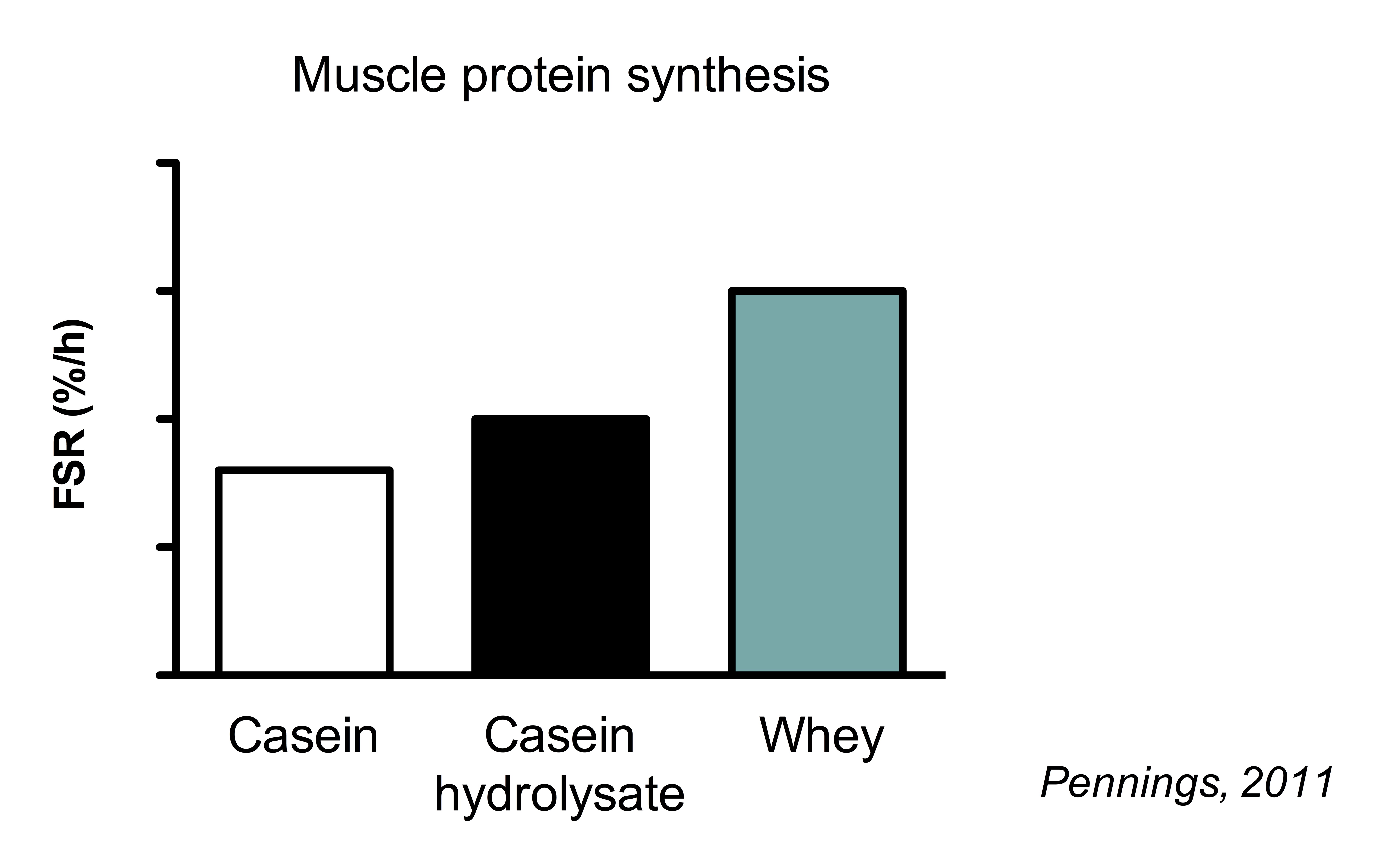
It resembles the digestion of a fast digesting protein. Consequently, Whey Protein results higher MPS rates than intact casein.
However, the muscle protein synthetic response to hydrolyzed is lower than that of whey protein. While both proteins are fast digesting, whey protein has a higher essential amino acid content (including leucine)
IS WHEY PROTEIN GOOD FOR YOU?

As you have read earlier whey protein is a complete source of protein and it has many health benefits as well as very helpful for people who are involving in some kind of resistance training.
Apart from his complete source its fast digesting as well as the bio availability is high.
According to some researches, It has been seen that there is no such benefit of whey protein supplementation in untrained individuals in healthy adults.
So if you are not into any type of resistance or endurance training there is no such benefit of taking whey protein supplement, you are able to hit your daily protein intake through food only. If you are taking.
Whey protein powder in a sedentary lifestyle the amount of protein powder you are taking will be considered as extra.
According to a 2017 study, excessive consumption over a long period of protein supplementation may have some adverse effects on the body, which is aggravated when associated with sedentary lifestyle.
Analysis revealed that chronic and without professional guidance use of whey protein supplementation may cause some adverse effects specially on kidney and liver function.
SIDE EFFECTS OF WHEY PROTEIN

The kidney and the liver play a central role in protein metabolism. Synthesis of albumin and other proteins occurs mainly in the liver, whereas protein breakdown and excretion are handled through an intricate interaction between these two organ systems.
Long-term consumption of a high-protein diet could be linked with metabolic and clinical problems, such as loss of bone mass and renal dysfunction.
However, although it is well accepted that a high-protein diet may be detrimental to individuals with existing kidney dysfunction, there is little evidence that high protein intake is dangerous for healthy individuals.

High-protein meals and foods are thought to have a greater satiating effect than high-carbohydrate or high-fat meals.
Results conflict and do not allow any conclusion about kidney-damaging effects of long-term, high-protein intake.
A meta-analysis of a group of prospective randomized trials including over 2,000 patients found a significant effect on reducing dietary protein decreasing the risk of end-stage renal disease or death (defined as renal death).
Whey does not harm the liver or kidneys, but it can exacerbate pre-existing damage. People with damaged livers or kidneys should exercise caution when increasing protein intake quickly without the guidance of a doctor.
IS WHEY PROTEIN BAD FOR YOU?
Eating a high-protein diet doesn't appear to harm the kidneys or liver unless there is pre-existing damage and dysfunction.

It's possible that dramatically increasing protein intake in a short timespan can lead to adverse effects on the liver and kidneys, but evidence for this is lacking. Bone health also appears to be either largely unaffected or benefited by eating more protein.
Don't worry about it if you have healthy kidneys and control your protein intake if you have damaged kidneys. It may be prudent to gradually increase protein intake to higher levels rather than jumping in both feet at a time, but there isn't much on this topic.
It is generally recommended to consume more water during periods when protein intake is being increased. Whether or not this has biological basis is not known, but it may be prudent to do.
BEST TIME TO TAKE WHEY PROTEIN SUPPLEMENT
There is no specific time to take protein, you can take it anytime during the day. Just HIT THE DAILY PROTEIN INTAKE, its only the overall nutrition that matters.

But there are some studies suggest that, taking Whey Protein in a specific time will give you additional benefit. Some researchers have gone so far as to claim that the timing of nutritional consumption is even more critical to muscle development than the absolute daily consumption of nutrients.
Nutrient timing involves manipulation of nutrient consumption at specific times in and around exercise bouts in an effort to improve performance, recovery, and adaptation.
Using this approach, it is argued that the concept of nutrient timing is constrained by reliance on interpretation of an "anabolic window" and may be better viewed as a "garage door of opportunity" to positively impact performance, recovery, and athlete availability.
Exercise improves the muscle protein synthetic response to protein ingestion. Therefore, it has been suggested that protein intake immediately post-exercise is more anabolic than protein ingestion at different time points.
- A meta-analysis concluded that protein supplementation ≤ 1 hour before and/or after resistance exercise improved muscle mass gains (Schoenfeld, 2013). However, this effect was largely explained by the fact that the protein supplementation increased total protein intake, rather than the specific timing of protein intake.
Protein ingestion following resistance-type exercise stimulates muscle protein synthesis rates, and enhances the skeletal muscle adaptive response to prolonged resistance-type exercise training. As the adaptive response to a single bout of resistance exercise extends well beyond the first couple of hours of post-exercise recovery.

2. Protein ingested prior to sleep is effectively digested and absorbed, and thereby stimulates muscle protein synthesis rates during overnight recovery. Recent studies investigating the impact of pre-sleep protein ingestion suggest that at least 40 g of protein is required to display a robust increase in muscle protein synthesis rates throughout overnight sleep.
In short, Pre-sleep protein ingestion represents an effective dietary strategy to improve overnight muscle protein synthesis, thereby improving the lean muscle mass response to exercise training.
IS WHEY PROTEIN SOMETHING MAGICAL?

Many people think that consuming whey protein will help you in build muscle or loose fat faster but its not the actual case. Building a impressive physique or loosing a lot of fat depends on various things like Genetics, Calories you are consuming, you activity level and the last thing which is most important is CONSISTENCY.
Whey protein is not something magical which will help you in instantly build muscle or loose fat or look great.
Supplementing Whey protein will help you hitting your daily protein intake goals will will lead to increased in lean mass and strength but noticing a visual progression will also take a lot of time(YEARS).
CONSLUSION
Whey protein is a type of protein which is usually present in milk. Whey protein is known for its fast digesting and absorbing properties. Apart from that whey protein is a complete source of protein which means it has all the Essential Amino Acids which is needed for our growth and overall development of our body.
Whey Protein is the water-soluble part of milk. As a supplement, it’s sold as dry powders with various levels of processing that affect how concentrated a source of protein they are and how fast they’re absorbed.
The main benefit of whey protein supplement is that it can help you to hitting your daily protein intake without consuming the extra calories from food. It is recommended that supplement should be only account for 10-15% of the daily caloric intake.
Whey Protein is capable of enhancing lean mass accretion with resistance exercise and attenuating the loss of lean mass during periods of energy deficit,
It was found that, Protein Supplementation in combination with resistance training was associated with gains in fat-free mass. Combining protein supplementation with resistance training is effective for eliciting gains in fat-free mass among older adults, but does seem to increase muscle mass or strength but in a very small amount.
This review suggests that protein supplementation may enhance muscle mass and performance when the training stimulus is adequate (e.g., frequency, volume, duration), and dietary intake is consistent with recommendations for physically active individuals.
when protein supplements are provided, acute changes in post-exercise protein synthesis and anabolic responce can be seen researches also have been shown have resulted in measurable reductions in muscle damage and enhanced recovery of muscle function.
Muscle protein synthesis is the process of building specifically muscle protein. It resembles the digestion of a fast digesting protein. Consequently, hydrolyzed whey results higher MPS rates than intact casein.
However, although it is well accepted that a high-protein diet may be detrimental to individuals with existing kidney dysfunction, there is little evidence that high protein intake is dangerous for healthy individuals. High-protein meals and foods are thought to have a greater satiating effect than high-carbohydrate or high-fat meals.
WHEY PROTEIN YOU CAN BUY
1 KG
MUSCLE BLAZE: https://amzn.to/3oHj6vM
AS-IT-IS: https://amzn.to/3yyzgw3
BIGMUSCLE NUTRITION: https://amzn.to/34hQe3H CRUDE WHEY: https://amzn.to/3488Wel
2 KG
BIG MUSCLE NUTRITION CRUDE WHEY: https://amzn.to/3fjFoAV
MUSCLE BLAZE FUEL ONE: https://amzn.to/3fe1ZyL
MUSCLE BLAZE RAW WHEY: https://amzn.to/348kEWa
MUSCLE BLAZE WHEY GOLD: https://amzn.to/3fepHL5
5 KG
AS-IT-IS RAW WHEY: https://amzn.to/3ugEGbN
MUSCLEBLAZE RAW WHEY: https://amzn.to/3uc4ZzH
SCITRON ADVANCE WHEY PROTEIN: https://amzn.to/3yytTwK
MUSCLE BLAZE CHOCOLATE FLAVOUR: https://amzn.to/2QIEFQ0
OPTIMUM NUTRITION GOLD (PREMIUM): https://amzn.to/3ufxbBU
REFERENCES
https://examine.com/nutrition/whey-protein-and-efficiency/
https://examine.com/supplements/whey-protein/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27653283/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23645387/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25355074/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32702243/
https://examine.com/nutrition/can-eating-too-much-protein-be-bad-for-you/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24299050/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23241341/
https://examine.com/guides/protein-intake/
https://examine.com/nutrition/protein-intake-calculator/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11507179/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27916799/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30702982/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32629950/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23645387/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30848096/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30824459/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24435468/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25169440/
https://examine.com/nutrition/can-eating-too-much-protein-be-bad-for-you/




Comments
Post a Comment